Study of Water Vascular System of Starfish
Title:- Study of Water Vascular System of Starfish
Water Vascular System :-
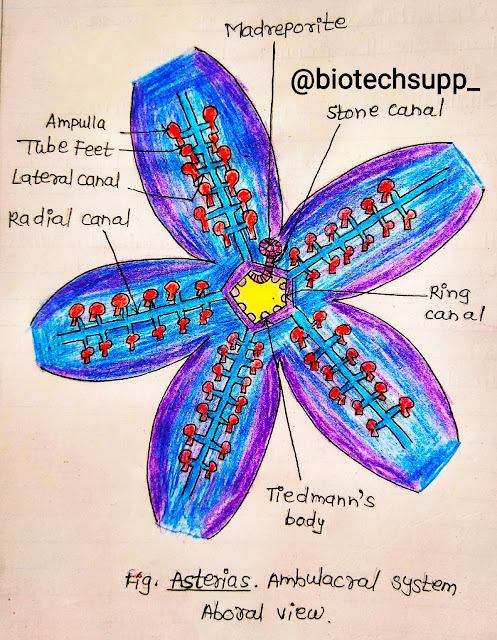
The water vascular system or ambulacral is sort of hydraulic pressure mechanism and consist of madreporite, stone canal, ring canal, radial canal, Tiedmann's bodies, pollian vesicle, Lateral canal & tube feet. This system concern with locomotion.
1)Madreporite - A flat disc with radiating grooves at the bases of bivium It is hard, rounded, Calcarious plate on the aboral surface. It leads to stone canal.
2)Stone Canal - A ampulla, opens into a vertical 'S' shaped stone canal. It is a cylindrical tube. Supported by calcarious rings. The stone canal runs downward from madreporite to join ring canal.
3)Ring Canal- It is a wide, five sided or pentagonal, ring like canal situated around mouth. It lies just inner side of the peristomal ring.
4)Tiedmann's Bodies - The ring canal gives off inter-radially a pair of small vesicles on it's inner side called racemose gland or Tiedmann's Bodies. These are small, yellowish rounded bodies. There are only nine Tiedmann's bodies, 10th being absent & it's position taken by stone canal.
Tiedmann's bodies manufacture the amoebocytes which are phagocytic in function.
5)Pollian vesicles - The ring canal gives off in each inter-radius a large, thin walled pear shaped Sac called Pollian vesicles. There number is variable from 2 to 4. These are contractile structures with stores water & suppose to regulate the pressure in water vascular system & manufacture amoeboid cells.
6)Radical Canal - Ring Canal from it's outer surface gives off five, long, ciliated radical canals into each arm. These canals runs upto the tip of arm.
7)Lateral Canal - During the course of radial canals it gives off on either side a series of short, narrow, transverse branches, called lateral or Podial Canals. They are arranged alternately long and Short & open into tube feet.
8)Tube Feet - There are two alternating rows of tube feet on either side in ambulacral groove of each arm. Each tube feet or podium is a hollow, elastic, thin walled sac like part is called Ampulla, a middle Podium & lower disc, like structure- Sucker.
The ambulacral system (water vascular system) mainly helps in locomotion, adherence to substratum & plays an important role in Respiration.
•Temporary Preparation of Gonads from starfish:-
Asterias is unisexual animal. The male gonads (testis) & female gonads (ovaries) have similar form & structure but they differ in colour. The testis are pale gray while ovaries are pink to orange in fresh state.
•Location - There are pair of Gonads. Each pair is lie free laterally in the base of each arm between pyloric caeca & Ampullae.
•Structure - Each gonad is branched structure Consisting a masses of small rounded follicles like bunches of grapes.
-------------------------------------------------------------------
•Study of T.S of an arm & Types of Pedicellariae:-
•T.S. Passing through arm of starfish :-
1)The arm is covered by cuticle, ciliated epidermis & thick dermis.
2)The dermis contains numerous perihaemal spaces and oscicles.
3)Epidermis and dermis shows spines, Pedicellariae and dermal branchiae.
4)In the T.S. the aboral surface appears thick and convex arch while the oral surface is like an inverted 'U' shape.
5)The arm encloses Coelom which contains a fair of pyloric Caeca, each suspended by two longitudinal mesenteries from the aboral surface.
6)On the oral surface ambulacral groove is Supported by two elongated ambulacral ossicle meeting at summit of groove.
7)Above the ambulacral groove runs a radial canal which is jointed on each side by podial branch to two ampullae called lateral water Canals.
8)A radical hyponeural sinus is seen below the radial canal.
•Types of Pedicillariae :- The pedicillariae are modified spines that occur in space between spines in clumps around bases of spines all over the body. They are microscopic pincer like or jaw-like bodies.
• Structure of Pedicillariae :-
The stalked or pendunculate type of pedi cillariae are found in the genus Asterias. Each Pedicellariae consist of short, Flexible & fleshy stalk, but there is no internal calcarious Support. The stalk bears three calcarious plates or ossicles, a basilar Plate at it's top & two jaws or valves. The jaws are articulated with basilar plate & serrated along their opposed edges. The pedicellariae having three calcarious pieces & stalk are called forcipulate pedicellariae. They are covered with epidermis which is richly supplied with sensory & gland cells.
•Types of pedicellariae :-
There are two types of forcipulate pedunculate Pedicellariae found in Asterias. These are foreceps or straight type of scissors or Crossed types.
•Foreceps or Straight Type :-
It is simple type in which the two jaws are more or less straight & attached basically to the basal piece. When Pedicellariae is closed the jaws remain parallel & meet throughout their length like Foreceps. The jaw can be opened or closed one pair of abductor muscles to open them.
•Functions of Pedicellariae :-
The pedicellatide Perform different functions. They are useful for the Protection of delicate skin, gills or papulae & kept the body surface free from debris & foreign organisms. They also serves as defensive & offensive organs.
•Study of larval forms in Echinodermoda:- (Bipinnaria Lava )
1)This is the free living larval stage of Asteroidea.
2)Bilaterally symmetrical & somewhat angular in shape.
3)The anterior end of larva is enlarged to form a Pre-oral lobe. The ciliated border of pre-oral lobe is Called Pre-oral bond which encircles the mouth. The pre-oral bond separates completely from rest of the longitudinal bond or post-oral bond.
4)The larva develops three lobes on either side of body which are bordered by post- ciliary bond.
5)The larva is free-swimming.
6)The larva shows the mouth, oesophagus, stomach and intestine.
7)The bipinnaria larva changes into the next larval stage called branchiolaria larva.
_______________THANK YOU_______________








Post a Comment